Describe the General Structure of Dna
A closer look at the chemical structure of DNA shows four main building blocks. Describe the structure of DNA molecule including general shape three nucleotide components and types of bonds between base pairs.
A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides A DNAmoleculeconsists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotidesubunits.

. DNA is a polymer of deoxyribonucleotides or simply deoxynucleotides. Phosphodiester bonds in DNA polymers connect the 5 carbon of one nucleotide to the 3 carbon of another nucleotide. Each type of nucleotide has a different nucleobase stuck.
Using research from many sources including chemically accurate models Watson and Crick discovered how these six subunits were. Briefly describe the underlying structure of chromosomes including nucleosomes Question. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Describe the functions of DNA. Watson and Crick proposed that the DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix called a double helix. 6 rows The structure of DNA can be understood in three stages.
Key information only 22 of human DNA are coding sequences. The molecular structure of DNA The four nucleotide monomers are distinguished by their bases. Core elements and regulatory elements.
Base-pairing takes place between a purine and. A 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a. Its structure is described as a double-stranded helix held together by complementary base pairs.
A twisted ladder composed of Double Helix FUNCTION. Holds genetic codeinfo genes and instructions for making proteins. What are the three steps of DNA replication.
In 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the DNA structure. In its natural state each DNA molecule is actually composed of two single strands held together along their length with hydrogen bonds between the bases. DNA also includes sugars and phosphate groups made of phosphorus and oxygen.
Describe the Basic Structure of DNA. It is composed of the 5 - carbon sugar deoxyribose a phosphate group and one of several organic nitrogenous bases. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating groups of sugar deoxyribose and phosphate groups.
The structure of DNA is a double helix Hydrogen strand. The core elements or sequences actually take parts in protein formation. DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for growth and development in every living thing.
The chemical structure of DNA the. It is composed of monomeric units namely deoxyadenylate dAMP deoxyguanylate dGMP deoxycytidylate dCMP and deoxythymidylate dTMP It may be noted here that some authors prefer to use TMP for deoxythymidylate since it is found only in DNA. Chromosomes are made.
In general the gene structure consists of two types of elements. The nitrogenous bases of the two separate polynucleotide strands are bound together according to base pairing rules A with T and C with G with hydrogen bonds to make double-stranded DNA. A molecule of DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure.
DNA is a long molecule made up of units called nucleotides each nucleotide is made up of three basic components. Start studying Describe the general structure of DNA. Describe the Significance of DNA Structure.
Double helix is the description of the structure of a DNA molecule. Hydrogen bondsbetween the baseportions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together Figure 4-3. Each of the two strands is a long sequence of nucleotides or individual units made of.
DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a. DNA is composed of subunits that are made of a sugar a phosphate and a base. The two DNA strands are separated by the DNA helicase.
Adenine A Thymine T Guanine G and Cytosine C. Describe the structure and complementary base pairing of DNA. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain or a DNA strand.
A molecule of DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure. The four bases associated with DNA are. The replication of DNA begins at a point known as the origin of replication.
The overall structure of a strand of DNA resembles that of a twisted ladder with. We call these nitrogenous bases. Describe the structure and function of DNA.
These make the phosphate-deoxyribose backbone. Exons are core elements. While the regulatory elements maintain gene expression.
DNA is a two-stranded molecule that appears twisted giving it a unique shape referred to as the double helix. Diagram the structure of a. The double helix looks like a twisted ladder the rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases base pairs and the sides of the ladder are made up of alternating sugar molecules and phosphate groups.
The Structure of DNA The Double Helix DNA is made up of six smaller molecules -- a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate molecule and four different nitrogenous bases adenine thymine cytosine and guanine. A DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic information.

Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology

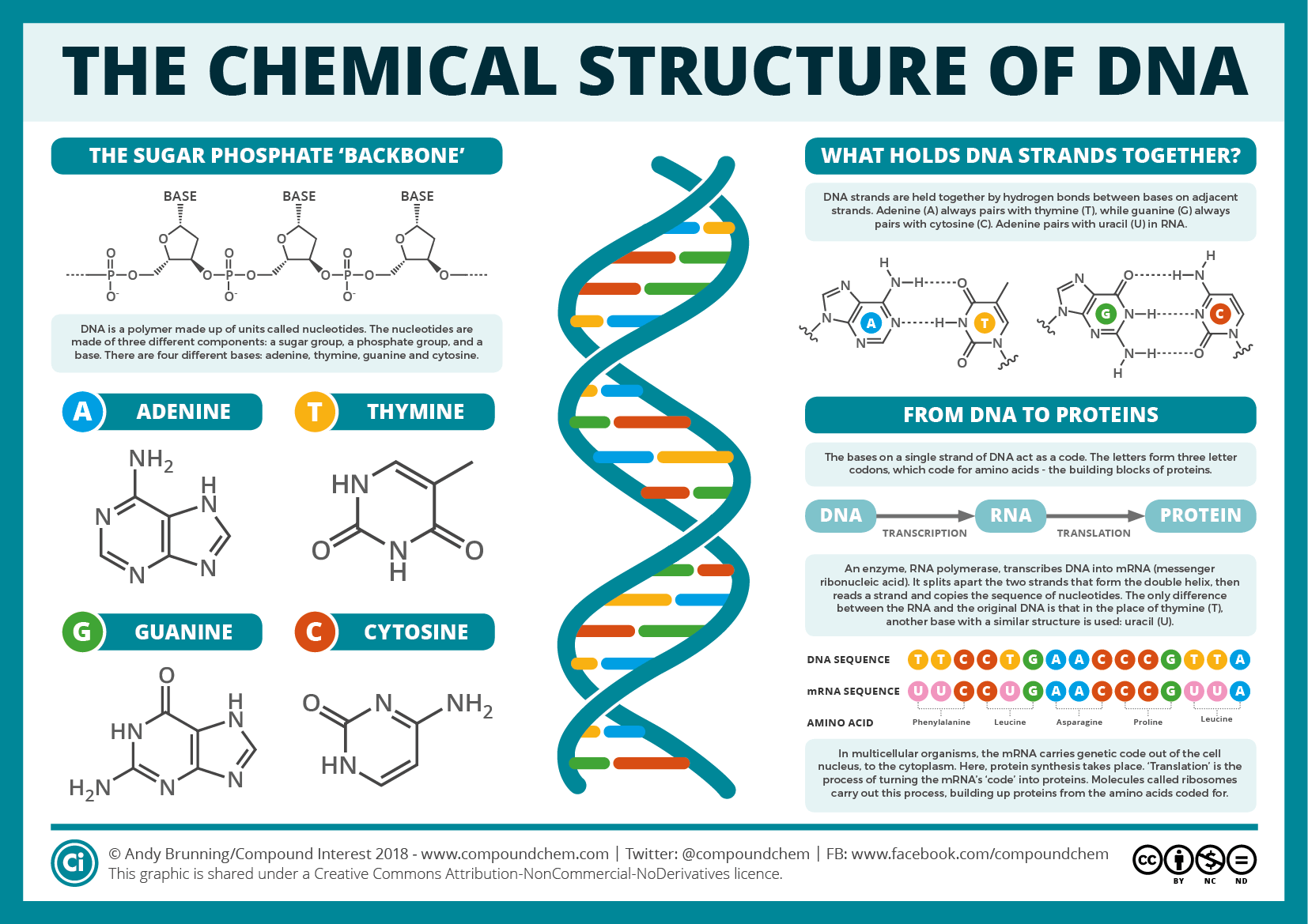
No comments for "Describe the General Structure of Dna"
Post a Comment